Python Environment Setup for Implementation
Python is a good scripting language to boost your productivity on data analysis and BI reporting. As open source language, you can easily get the binary installation file from python official site for windows and source code on vary versions for Linux, in production, it’s better choose installation approach by source code.
We also need to setup python environment after installation so that we can not only use python interpreter to develop but also make it executable by CLI and even some ETL tool such as Microsoft SSIS.
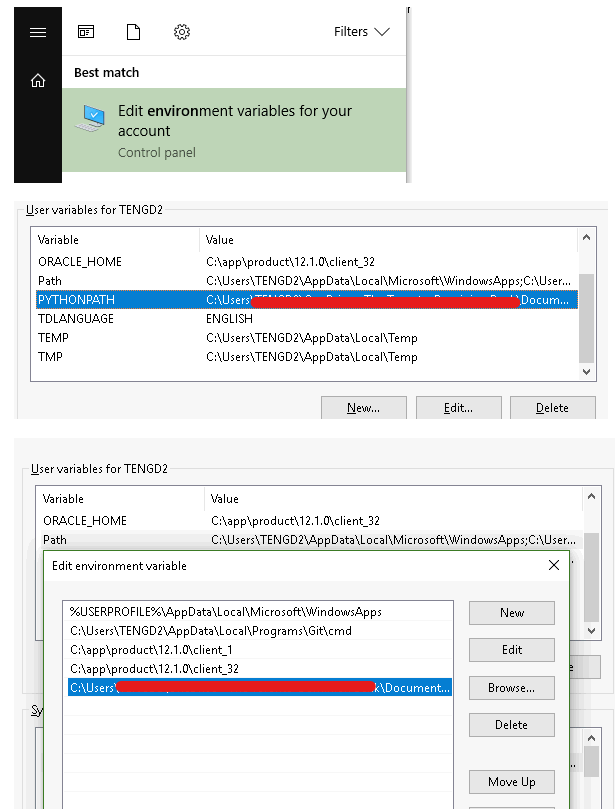
Python environment variable configuration and local folder set up for your file, package and library
If python is installed in system-wise, then you need to create some new folders to store you python file, package and library, e.g. python install path is “D:\Python36", then you need to add python executable interpreter to be a part of the PATH variable. Next create python environment variable PYTHONPATH with the following paths and create empty file __init__.py file in each of these folders:
- create a new folder under D drive “D:\pyLib” and set that directory as value of PYTHONPATH and create __init__.py file in “D:\pyLib”
- you can also create subfolder to assign different permissions for different user group
- create a subfolder “D:\pyLib\AD-group1” and create the __init__.py file in it.
- create a subfolder “D:\pyLib\AD-group2” and create the __init__.py file in it.
For Linux, if you install python3 by source code and directory is /usr/local/python3, then edit ~/.bash_profile file, append the python directory into PATH
1 | # Python3 |
then run source ~/.bash_profile let setting take effect
if your system pre-installed python2 then it’s necessary to make a soft link
1 | ln -s /user/local/python3/bin/python3 /user/bin/python3 |
setup name space and package python scripts for development project to be able to importable
- create or edit environment variable and add your python files folder into your system directory
- enter your python file folder to create an empty file __init__.py file
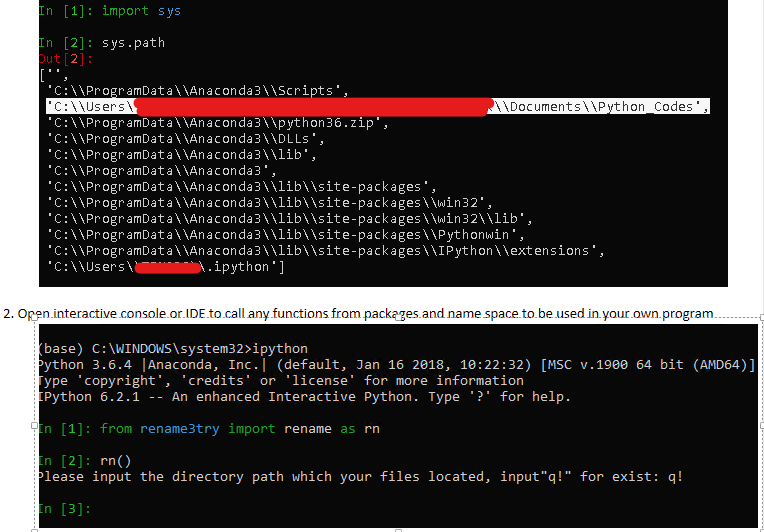
- open terminal prompt type python to active python interactive console
- import sys
- execute sys.path to make sure your python file folder is recognizable by python
Python readiness test in localhost for SQL database connection (Anaconda virtual environment)
First check python and Ipython version by issue command python --version and ipython --version. Anaconda almost pre-installs all python prevailing and popular libraries in its virtual environment, to check library list by using command pip list
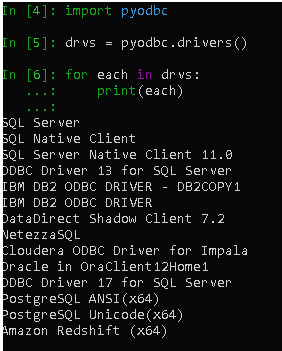
Python and SQL database connection facility with supported drivers
Depends on what python library do you install for database connectivity, it usually comes with function to show you available drivers to connect python to your database, e.g: pyodbc, use drivers() function to list the odbc drivers
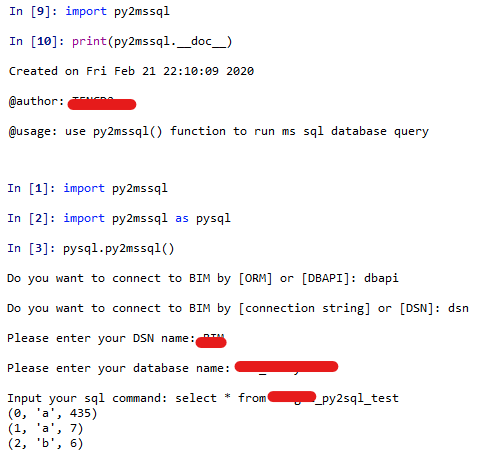
Python SQL Server database connection and data task
SQL Server database can be connected both by DB API (pyodbc) and ORM (sqlalchemy), create a py script and run sql query from user input
1 | import pyodbc |
script both can be ran directly or imported (recommend) after setup PYTHONPATH variable in your account and copy that script over to the path of environment variable.
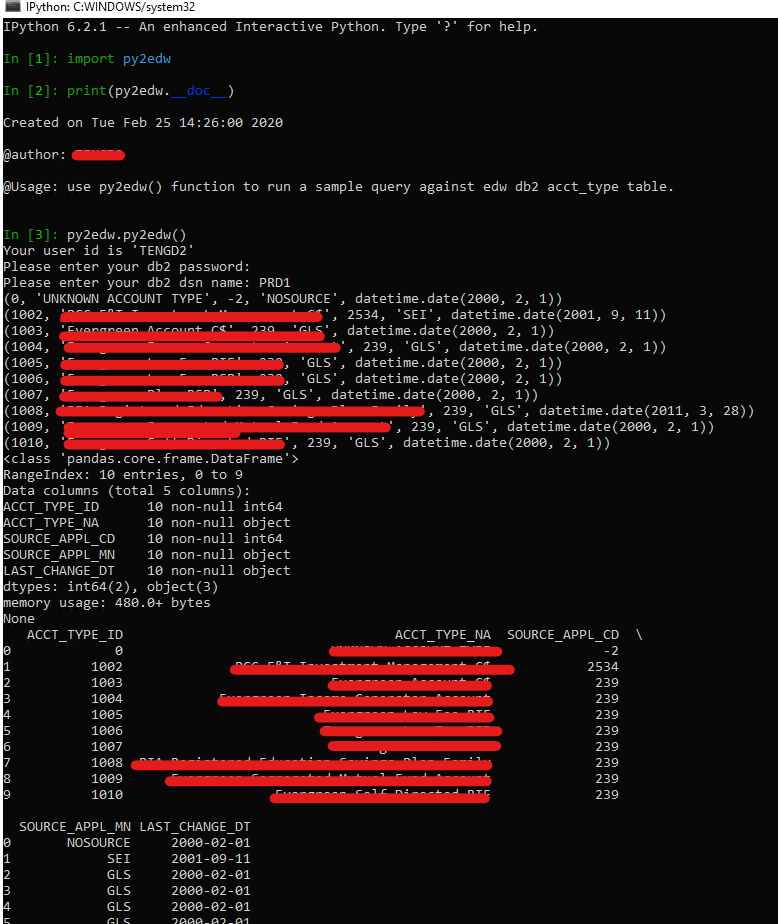
Python DB2 database connection and data task
We can only connect to DB2 by DBAPI (pyodbc), connection string doesn’t work but only DSN (PRD1 was setup as system DSN in local and server) plus user id and password. Use below script to try to connect
1 | import pyodbc |
one thing need to be aware is the script better runs on the shell than python interactive console because pyQT doesn’t support password masking
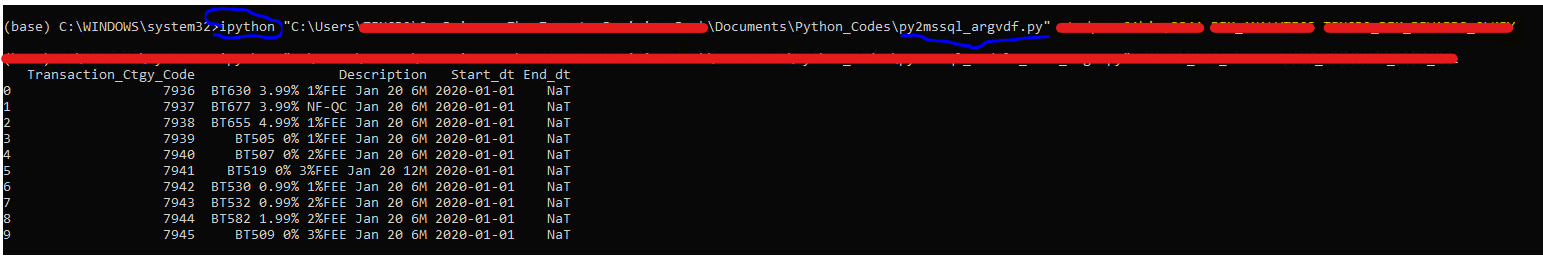
Productionize Python script by passing in parameters
In this section we will demonstrate how you can parameterize your code in python or pyspark so that you can use these techniques before deployed your script into production for automation. It’s best practice to parameterize database names, tables names, and dates so that you can pass these values as inputs to your script. This is beneficial when writing code for values that are dynamic in nature, which can change depending on the environment and/or use case.
The key module is from python standard library: sys. Assign variables through sys.argv[...]
1 | import pandas as pd |
run python script in CLI (command line interface) by following parameter values
1 | ipython py2mssql_argvdf.py yourSvrNm yourDBNm yourTblNm |
Encapsulate into SSIS to minimize change in production deployment – python interpreter
An alternative way to apply python in production is leverage current SSIS package and embed python script in process task
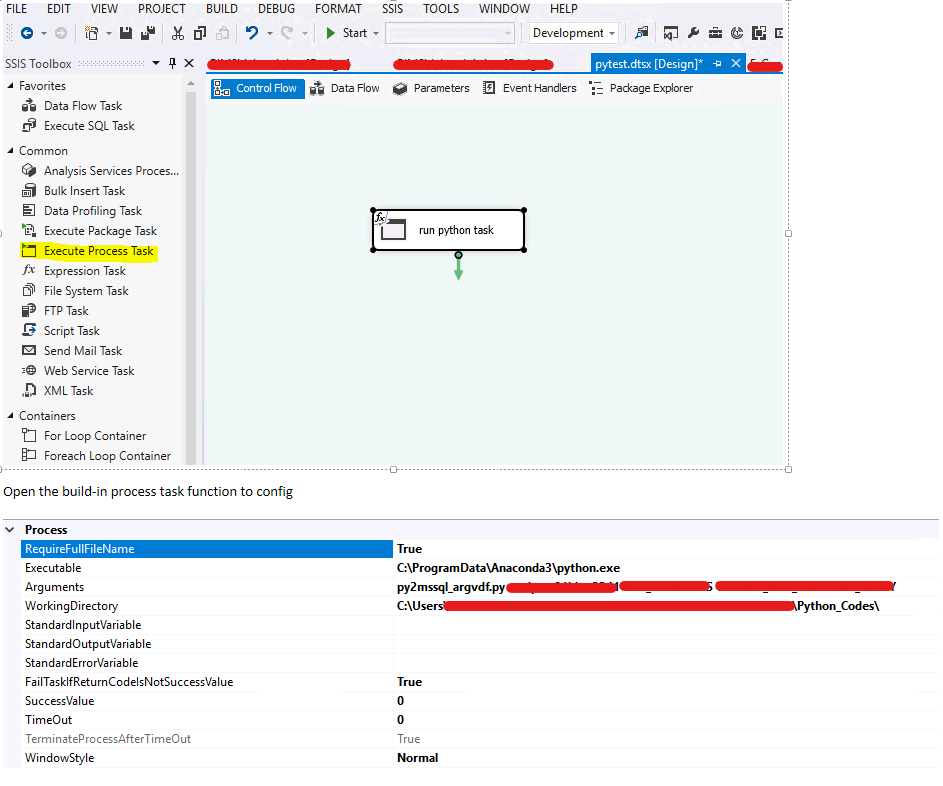
you can hard code the configuration or use expression (VB) through variables in package
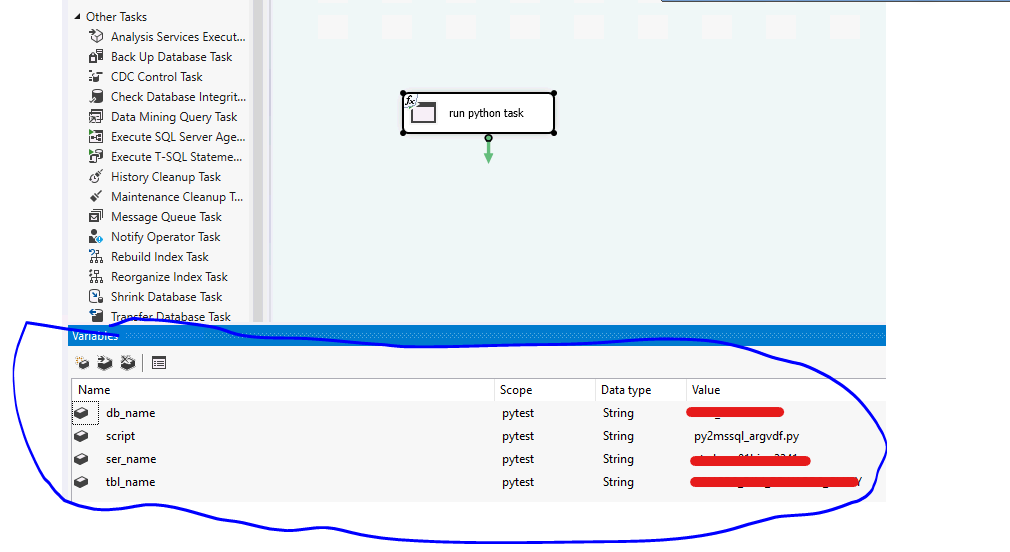
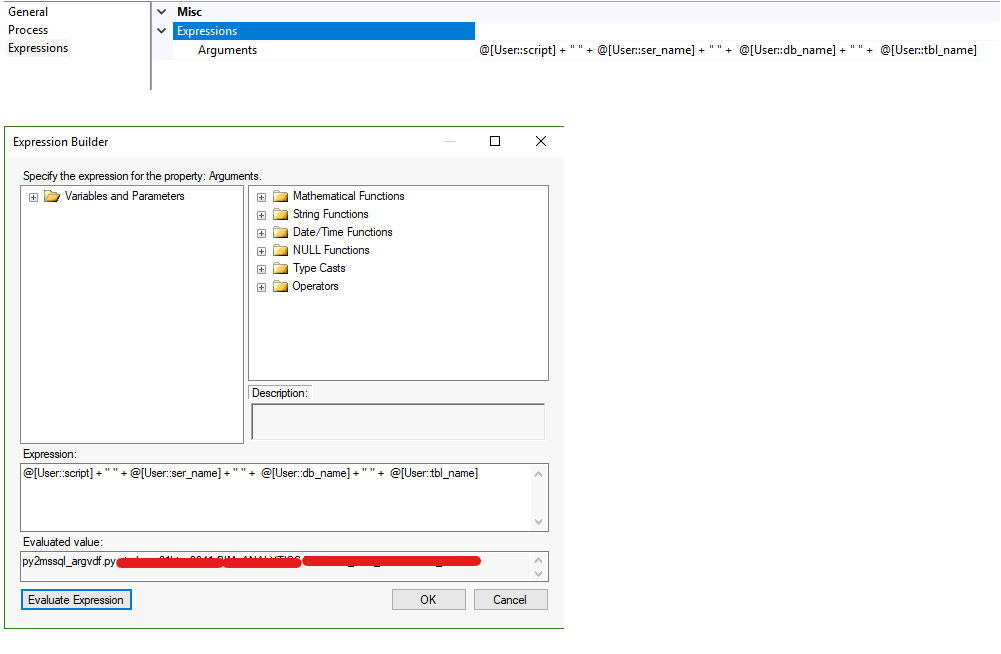
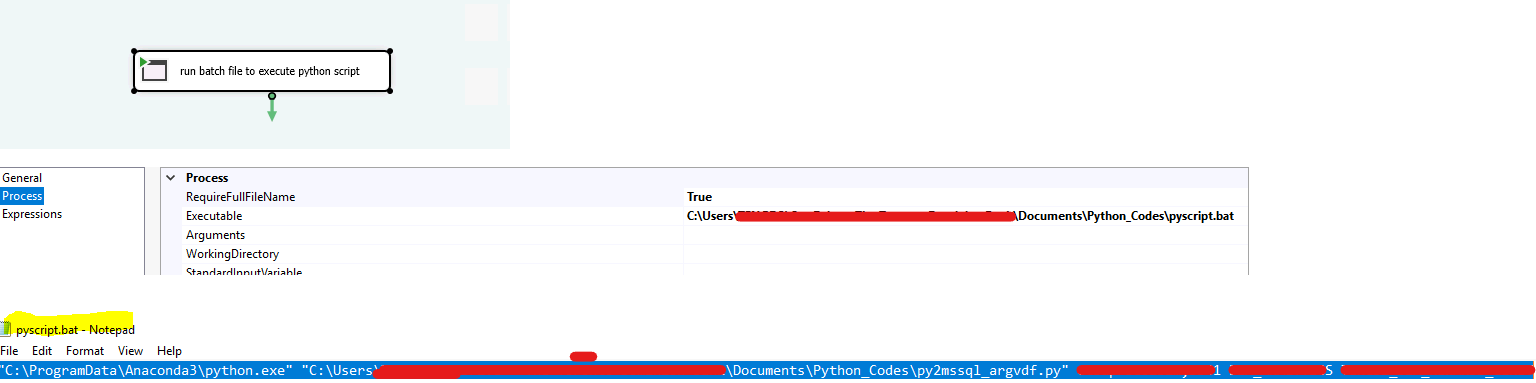
Encapsulate into SSIS to minimize change in production deployment – batch process
use batch process by .bat file also can achieve that task
Call user defined module or function in python script
It’s very efficient to create bunch of generic module packages to contain functions to be used widely by other python scripts for specific tasks.
| 1. | Firstly, setup python environment variable to include directories which are recognized by python |
|---|---|
| 2. | Create __init__.py file (can be empty) in these folders |
| 3. | Create python programs and save script should end up with if __name__==”__main__“: main() |
| 4. | Ready to import user modules and functions |
1 | import pandas as pd |
