Hadoop Data Side Load from SQL Server
Agile development and DevOps bring flexibilities and quick solutions to support business intelligent in timely manners. A technical platform and its associated applications and tools are able to turnaround very quick so that business analysts and data scientists would be able to leverage them to do the data modeling or machine learning, but in the other side, unlike functions buildup, data sync across different platforms is not that easy and quick especially for large organizations.
Background and the gap of data modeling for Hadoop early adopter
These years, big data and Hadoop are kind of trend for next generation data technic. Many companies adopt that as major data platform, but the most of data is still allocated in RDBMS data warehouse, business intention is to leverage high quality data in SQL database to build their analytical work in Hadoop, the data consistency is the first consideration from data perspective, but it is not a easy task because data is going to migrate to different platform with different operating system (from Windows to Linux). Technically, the best solution for the project is the build the direct connection from SQL Server and SSIS to Hive by using Apache Sqoop or utilize the JVM to build JDBC connection by JAVA, but for large organization, applying a new tool on production needs a quite lot approve work; developing JDBC connection facility also needs multiple level testing, those are taking a long time.
Therefore the solution is back to the foundation of the Hadoop - file system. Because SSIS cannot write to Hive directly using ODBC (before 2015 version). The alternative is to create a file with the appropriate file format and copy it directly to the Hadoop file system then use Hive command to write metadata to Hive metastore, the data will show up in the Hive table and also available in Cloudera Impala.
File operation for data migration from SQL to Hadoop
In our case, moving files can be a litter more complex because of crossing different operating system and platform as noted earlier. In this case, we need t a way to execute the dfs -put command on the remote server. Server tools enable us to execute the remote processes. Hadoop is build upon Linux, so bash shell script to execute the remote process. But that is quite challenged in real operation in production environment.
- What if the number of files is huge and cannot done by manually issuing command but have to do the batch operation automatically.
- What if files being moved crossing multiple platform from Windows to Linux local file system to Hadoop file system and if the data would be able to keep the original value and format in Hive or Impala table.
Generate source data by CSV file from Windows side
For multi-processing, SSIS is the sounds solution and tool set on Windows side which enables us to run SSH commands on the remote server from an Execute Process Task. Setting up a package to implement this process is relatively straight forward. Just set up a data flow as normal with a source component retrieving data from SQL Server data warehouse. Any transformation actions that need to be applied to the data can be performed. Ad the last step of the data flow, the data needs to be written to a file. The format of the file is determined by what the Hive system expects. The easiest format to work with from SSIS is a delimited format, with carriage return/line feeds delimiting rows, and a column delimiter like a comma(,) or pipe (|) separating column values. The SSIS flat file destination is designed to write these types of files.

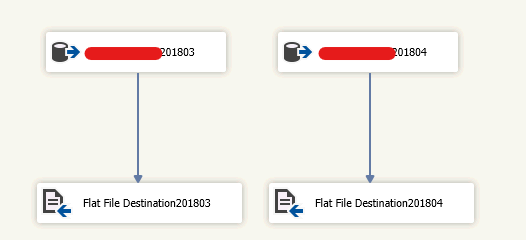
Automate file operation from Windows to Linux and HDFS
Once the file is produced, then use a file system task to copy it to a network location that is accessible to both SSIS server and Hadoop cluster. The next step is to call the process to copy the file into the HDFS. This is done through an Execute Process Task. It can be configured to use expressions to make this process more dynamic. In addition, if you are moving multiple files, it can be used inside a For loop in SSIS to repeat the process a specified number of times.
To FTP data file from Windows to Linux, we can use either sftp or scp command but first you should make sure you have Hadoop access. But the problem is when we copy data to Hadoop, we need to provide the password to access the system, so the process is manual. As mentioned before, for larger scale data migration, we have to figure out the way of automation so that silent mode is needed to avoid manually provide user password then we can use script to schedule job to automate data process.
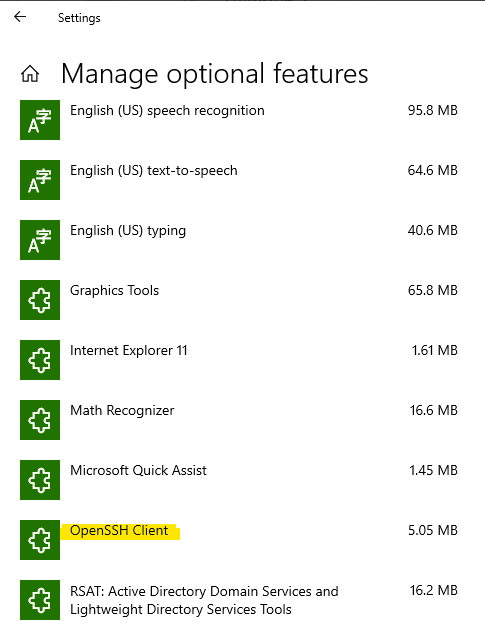
Check OpenSSH Client installed and enable in your machine
Open Windows setting -> App -> Apps & features -> Optional feature, check if OpenSSH Client is on the list, if not you need to install that client tool
On source side to create a public access key
This step we need use cmd prompt or git bash, open git bash, change directory to home folder by issuing command cd $HOME, you will find the hidden folder .ssh, you can display all folder by command ls -la
Issue below command to generate the public access key in order to enable the silent mode to Hadoop
1 | ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa |
tap 3 time enter key to generate the key, the value for argument -b is key size and has to be the number at least 2048, value of -t is algorithm. You will find the 2 new files are generated, id_rsa stores your identification information and id_rsa.pub is your public key which we need to copy to Linux server.
On target side FTP public key file to it
We can use scp command to upload public key to Linux server.
1 | scp -p 22 /home/yourUserName/.ssh/id_rsa.pub yourUserName@LinuxServerName:/home/yourUserName/.ssh/authorized_key |
You need to give password when issue above command to pass the authentication, but later this step will be bypass because of the public access key.
Load file from Linux file system to HDFS
Even Hadoop is installed on Linux, it has independent file operating system called HDFS, we need to issue command to transfer file between Linux and Hadoop. hdfs dfs command to manipulate Hadoop files, Hadoop is kind of remote server so we use -put argument to push file from Linux local to Hadoop; use -get to push file from Hadoop to Linux local, is this case we use put.
1 | hdfs dfs -put /yourLinuxFilePath/fileName.csv /HadoopFilePath/targetHiveDatabase.db |
Now, data file is in HDFS so that we can issue Hive command to write the table metadata into Hive metastore
Configure Hive table metadata to match up with SQL Server
In Hadoop side, we need to define Hive tables to store the data from SQL Serer. For keeping data consistency, we define the Hive table schema in terms of SQL table data type. We don’t use Ctrl-A(0x001) which is the default Hive column delimiter for flat file but use pipe bar(|) as field delimiter, because that isn’t supported well for use from SSIS in Window platform.
Now let’s dig a litter deeper on Hive data type which is the critical element and the most important consideration to keep data consistent. Hive provides a layer on top of Hadoop data that resembles a RDBMS. In particular, Hive is designed to support the common operations for data warehousing scenarios. Thanks to Hive to build the bridge between Hadoop MapReduce and RDBMS so that many of these data types have equivalent values in SQL Server, but only a few are unique to Hive.
| Type | Description | Examples | SQL Server Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Float | 4-byte single-precision floating point | 25.189164 | real |
| Double | 8-byte double-precision floating point | 25.1897645126 | float(53) |
| Decimal | A 38-digit precision number | 25.1897654 | decimal, numeric |
| Boolean | Boolean true or false | TRUE FALSE | bit |
| Timestamp | JDBC-compliant timestamp format YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS:ffffffffff | datetime, datetime2 |
define and create a Hive table is simple, the syntax just like SQL, but something different after all, it’s file system.
1 | create table yourTableName( |
If data files come with header then you need to tell Hive skip the first row by tblproperties. We save above script as createTbl1.hql then use Hive beeline command to generate table
1 | beeline -f ./yourPath/createTbl1.hql > /yourPath/hql.ot |
Load data file to Hive and Impala table
As long as we push data file to Hadoop and Hive directory, we can easily to write data to Hive table by issuing beeline -e command like below
1 | beeline -e "LOAD DATA INPATH '/HadoopFilePath/targetHiveDatabase.db/fileName.csv' INTO TABLE yourTableName" |
the metadata will be in the Hive metastore.
Cloudera Impala metastore is not sync with Hive automatically, so if you want to manipulate data in Impala, we need to issue impala command
1 | impala -q "invalidate metadata yourTableName" |
after that data is on both Hive and Impala table.
Automate the whole process
To get a better understanding of how the process looks like, below workflow illustrates how data file read from SQL Server side and load into Hive table in HDFS cluster.

now let’s create a script to bulk copy data file to Linux and save it as bulkcopy.sh
1 | scp -p 22 -r /yourDataFileFolder/ user@host:/home/user/dataFileFolder |
then for the task in Linux server side, we also create a script to push data from Linux local file system to HDFS then write data to Hive table and save it as bulkload.sh
1 | hdfs dfs -put /yourLinuxFilePath/fileName.csv /HadoopFilePath/targetHiveDatabase.db/ && |
so far, we have csv data file, bulkcopy.sh and bulkload.sh, now we will schedule a job to run those scripts automatically by using SSIS package
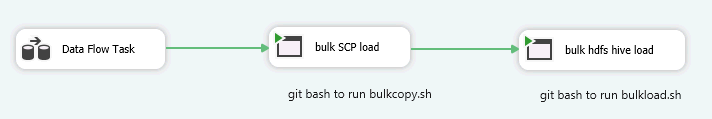
last, configure the SSIS package to write log data either file or database for debugging.
Both Hive table and Impala table will be good after run command invalidate metadata command in Impala shell for both HUE (GUI tool) and Linux server. Invalidate metadata command takes effect across both Impala shell and HUE web interface, but refresh command only tales effect on the environment the command run against.
Data restatement
It’s quite common practice in production to reload historical data with reconcile with new or changed logic or even correct some mistake so remove partial data and then reload is also important. Than task is easy for RDBMS but what if the same situation take place in Hadoop, there is no update statement in Hive or Impala, so we need to do multiple steps:
- Start state: number of data, e.g. 3 files need to restate in HDFS
- Issue command
hdfs dfs -rmto delete the 3 files with month_key (3 months) - Run query from HUE, make sure 3 month data and won’t impact other month
- Run above scripts and SSIS package add new 3 data files back again, then the data would be back to the Hive and Impala table
